Methods for Eliminating Tomato Hornworms: Exploring 5 Natural Strategies for Deterrence and Pest Management
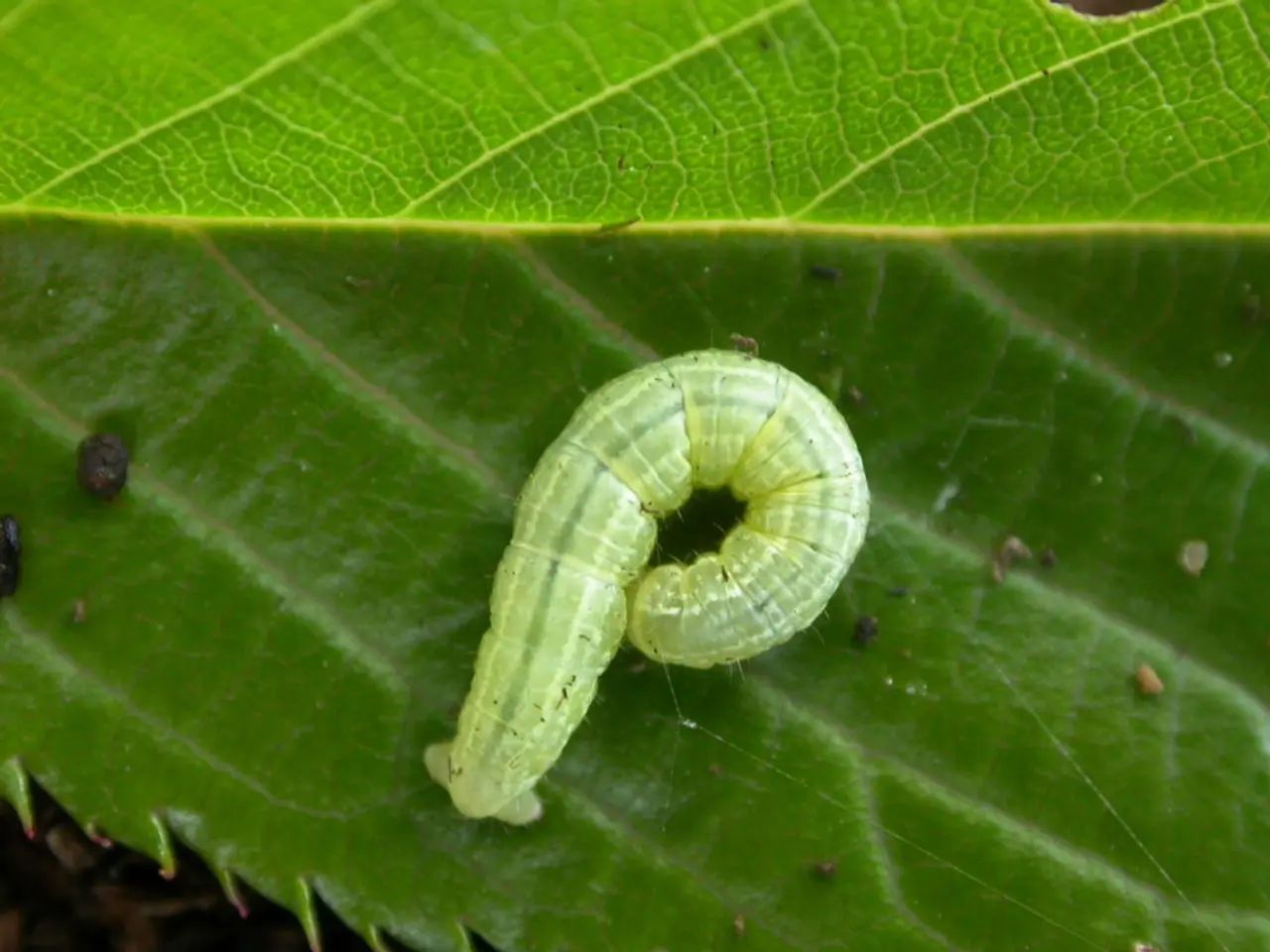
In the vibrant world of home gardening, the presence of pests like tomato hornworms can pose a significant challenge. These large green caterpillars, with white stripes forming V's and a dark green horn with black sides, can cause substantial damage to tomato plants, peppers, eggplants, and potatoes. However, there are several effective, natural methods to manage and get rid of tomato hornworms in a garden.
Handpicking is one such strategy. Regularly inspect plants for these large green caterpillars, carefully remove them wearing gloves, and dispose of them by dropping into soapy water or relocating far from the garden. This method is particularly effective during an active infestation, as tomato hornworms do not bite and their large size makes them easy to handle.
Another natural approach is attracting beneficial insects. Encourage parasitic wasps (notably braconid wasps), ladybugs, and lacewings by planting flowers and herbs that provide nectar and shelter. These predators naturally reduce hornworm populations by parasitizing or feeding on their larvae.
Companion planting is another strategy that can control pests, boost nutrients, and improve flavor. Plant deterrent species like marigolds and basil around tomato plants. Marigolds release pyrethrum, which repels moths that lay hornworm eggs, and basil deters pests directly. These plants also support beneficial insects that prey on hornworms.
Cultural controls such as crop rotation and clean cultivation are also essential. Practice crop rotation by avoiding planting tomatoes or related solanaceous crops repeatedly in the same spot, interrupting the hornworms' life cycle. Clean cultivation such as removing plant debris and tilling soil after harvest helps destroy overwintering pupae and reduces future infestations.
Additional methods include using garlic barrier sprays to deter moths laying eggs and biological insecticides like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) for severe infestations. Bt is a bacterium that causes disease in certain insects, paralyzing the hornworms' digestive system and leading to their starvation. It is harmless to humans and beneficial insects, but it will kill butterfly larvae, so use it only on affected crops with an active infestation.
Companion plants like borage, basil, marigolds, and nasturtiums can repel tomato hornworms and other pests while attracting beneficial and pollinating insects. To make a homemade spray with cayenne pepper, combine 1 cup of water, a teaspoon of dish soap, and 1/4 teaspoon of cayenne pepper in a bottle, then shake to mix. Spray the mixture over plants' leaves, including the undersides, several times per week, especially after it rains.
By employing these integrated natural methods, gardeners can create a sustainable approach to protect their tomato plants effectively from hornworms. Remember, a healthy garden thrives not just on the produce it yields, but also on the delicate balance of its ecosystem.
Maintaining a diverse home-and-garden, including flowers, herbs, and plants that attract beneficial insects, can help in managing tomato hornworms as these predators naturally reduce their populations.
Incorporating companion plants like marigolds, basil, and borage is another effective approach to repel tomato hornworms and other pests while supporting beneficial insects that prey on the hornworms.