Flora: Cohesion of Soil and Prevention of Erosion
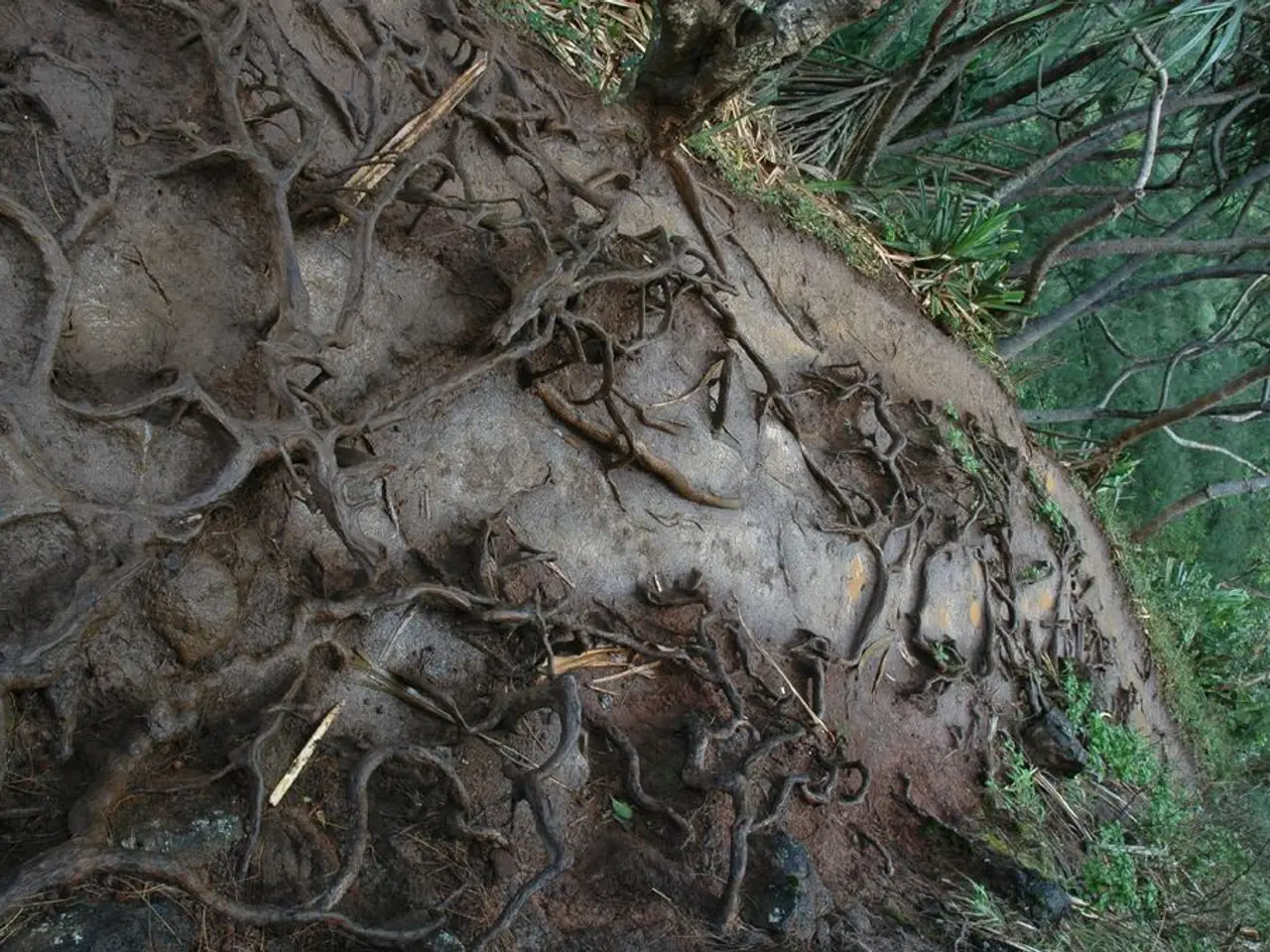
Plants play a vital role in preventing soil erosion, a problem that affects many parts of the world. By breaking the impact of raindrops on the soil surface, plants reduce the force of raindrops and hold the soil in place with their root systems.
The presence of plant stems influences the size and distribution of pore spaces in soil, which are essential for the movement of water and air within the soil, as well as for the growth and development of plant roots. Stems of plants can displace soil particles, creating pore spaces for water and air movement. Moreover, plant stems can secrete substances that bind soil particles together, creating aggregates and influencing the size and stability of pore spaces.
The physical structure of plant stems, including the presence of xylem vessels, acts as a thick barrier to water flow, slowing its movement and contributing to soil retention. The xylem tissues in plant stems are responsible for transporting water and nutrients throughout the plant. The xylem vessels in plant stems have different diameters, lengths, and perforations, which can influence the speed and direction of water flow.
Plants also help prevent soil erosion by acting as barriers. The stem of a plant can take up space, influencing the structure of the soil and the movement of water and air. Plant stems, by acting as barriers, help prevent soil from being washed away during heavy rain or strong winds. The root system of a plant functions like a web, anchoring the plant and the soil, and preventing it from being washed away during floods or strong winds.
In addition to their direct impact on soil erosion, plants contribute to soil fertility and plant nutrition through a mutualistic relationship with the soil. This relationship promotes soil fertility and plant nutrition, improving the overall health of the ecosystem.
In Germany, common plants used to prevent soil erosion include ground cover plants such as thyme, lavender, cranesbill geranium, and woolly betony, which help protect the soil by covering it and providing structure, especially in gardens. Additionally, green manure plants are widely used in agricultural settings to cover the soil, improve soil quality, and prevent erosion through deep rooting and nutrient retention.
The roots of plants absorb water and nutrients, promoting infiltration and reducing surface runoff. The creation of pore spaces by plant stems has a significant impact on the soil's ability to hold water and air. Furthermore, the presence of plants can also contribute to moisture retention and create a habitat for various organisms, further supporting soil stability and ecosystem health.
In conclusion, plants play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion, contributing to soil fertility, and supporting ecosystem health. By understanding and utilising the natural properties of plants, we can work towards sustainable solutions for soil erosion and promote a healthier environment.